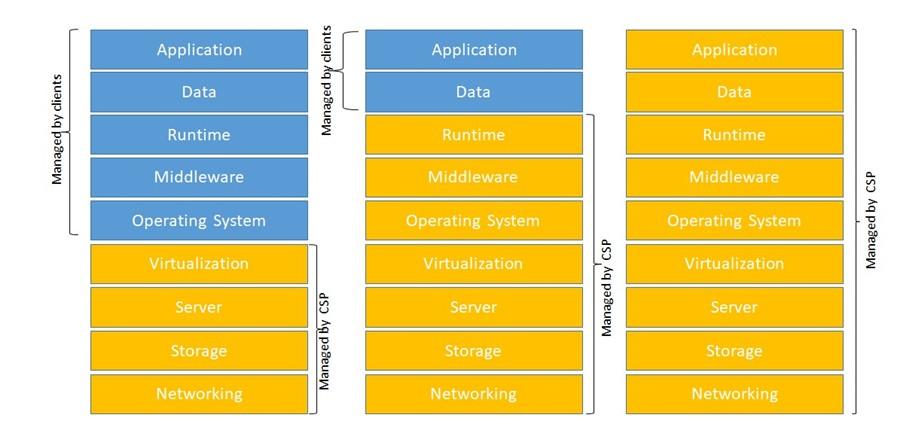
Cloud Service Model
There are many different types of cloud services, each involving different types of technology and assets. We give an overview below, we use this model later to indicate the different contribution of clients and cloud service provider.
Infrastructure as a Service
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) denotes to the essential requirements and building blocks of computing that can be rented, physical or virtual servers, storage and networking.
In IaaS the provider offers storage (virtual file systems) or computing resources (virtual CPUs), accessible online. Examples include Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud, Google’s Compute Engine, Amazon Simple Storage Service, Google Cloud Storage, Microsoft Windows Azure Storage, Rackspace, Dropbox etc.
Platform as a Service (Paas)
Platform as a service denotes to cloud computing services that supply an on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering, and managing software applications.
Platform as a service is designed to make it easier for developers to quickly create web or mobile apps,
without worrying about setting up or managing the underlying infrastructure of servers, storage, network, and databases needed for development.
Platform-as-a-Service provides tools and software that developers need to build applications on top of that could include middleware, database management, operating systems, and development tools. In Platform as a service, the provider distributes a platform for customers to run web and normal applications.
Software as a Service
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) is the distribution of applications-as-a-service and it is a method for delivering software applications over the Internet, on demand and typically on a subscription basis. With SaaS, cloud providers host and manage the software application and underlying infrastructure, and handle any maintenance, like software upgrades and security patching.
In Software as a service, the provider deliver complete application via the internet such as email servers ,email clients, document editors and customer relationship management systems. Users connect to the application over the Internet, usually with a web browser on their phone, tablet, or PC.

No Comments