IT- Disaster Recovery for a Business Continuity
IT disaster recovery consists of developing step-by-step procedures for a full recovery, disaster avoidance and business continuity.
When many think about DR, they usually think about Backup, while it is only one piece in BC-DR puzzle and inefficient for a continuity of business operations in an event of a disaster.
Backup is not disaster recovery (DR) based on following points:
- Failure of backup software
- Service Levels: backups typically happen twice per day which means that a RTO will be significantly higher and RPO could be ~12 hours data loss which is not acceptable for critical applications in DR concept.
- Reverse Replication: in an event of an outage, once an application has been made available on a target site, you must extend that application’s protection to include new data being created. A backup solution can not start taking backups and ship them back to a production site, yet a DR solution will ensure that an application is still protected by replicating back to a source site.
- Application Impact: backups occur at night because, making a copy of an application and its data load a CPU on a server and impacts significantly end-user productivity.
Every institution large or small should have both a backup mechanism and disaster recovery solution in place; they are complementary pieces to a same puzzle.
Mitigation Measures For Some IT- Hazards
|
POSSIBLE RISK |
MITIGATION MEASURE |
|
DOWNTIME
• Hardware • Software |
• Redundancy • Maintenance and upgrade of software |
|
NETWORK
• Unreliable network
• Loss of connectivity
• Traffic • Misconfiguration |
• Design and monitor a network for a maximum reliability • Physical protection, Redundancy or diverse paths • Network segmentation • Installation of firewalls to ensure security • Load balancing (Intelligent direction to backup site) • Use automation to deploy changes, test all configurations in a lab environment before making changes on your production devices. |
|
DATA AND APPLICATION
• File corruption • Application downtime • Malicious software |
• Data backup • Mirroring of application, load balancing and replication • Security management and installation of antivirus |
|
EQUIPMENT FAILURES
• Server failure • Server Overload • Other Hardware • Old equipment |
• Redundant disks, Backups, SAN / NAS • Load balancer/Monitoring/virtualization • Regular maintenance • Planning for upgrades and replacing out-of-date equipment. |
|
POWER
• Power Outage • Equipment failure |
• Redundancy and backup power supply (UPS and Generators) • Monitoring and performing preventative maintenance regularly. |
|
ATTACKS
• DDoS • Viruses • Hackers • Other attacks |
• Managed security services/anti-DDoS • Installation of antivirus • Firewall and other security features • Access control system |
|
HUMAN ERROR
• File deletion • Unskilled people • Fire |
• Regular backup • Access management • Training / Staff certification requirements • Fire detection system, fire extinguisher and fire hydrant |
Factors Influencing a Successful IT- Disaster Recovery
A. INFRASTRUCTURE
An infrastructure is a fundamental aspect which impacts and defines an output; an infrastructure condition or state should be well known in terms of network connectivity, quality, performance, processing capability and scalability.
Considerations at infrastructure layer:
- Before any hosting or connectivity, a required infrastructure including additional hardware and software especially needed for recovery and replication should be well defined and avoid single purpose infrastructure.
- Same Infrastructure on both sites(Primary and Alternative site)
- Availability of maintenance facilities
B. RTO AND RPO MEASUREMENT
RTO and RPO measurement should be based on a business impact analysis (BIA), conducted, that contain a classification and BIA matrix (criticality and priority level) of systems/Assets.
For critical systems RTO and RPO should be minimized to zero.
C. REDUNDANCY AND BACKUP
Backups and redundancy are both infrastructure and data protection methods, but which can not be replaceable and should be applied at every layer.
Redundancy is a data and system protection method considered as a real time fail prevention measure.
Backup does not provide real-time protection, but by performing restoration for it provides a protection against greater loss.
Data and system backup should be done regularly and kept offsite.
D. HIGH AVAILABILITY(HA)
HA is a disaster avoidance, a capability to automatically switch to alternative site without any downtime.
HA is achieved by applying:
- Clustering (mirroring of critical applications)
- Replication of clusters
- Load balancing in network which improves a HA by arranging multiple servers running simultaneously in primary and secondary order.
- Redundancy should be fairly implemented and sufficient at every layer (network, storage, etc.).
E. LEVEL OF DISASTER RECOVERY SITES
F. REPLICATION SOLUTION
Replication for disaster recovery (DR) is no longer a “nice to have” technology, but a necessary part of every disaster recovery solution.
Replication Mode
G. Virtualization
Software technique in which a single physical resource appears as multiple logical resources which reduce a data center complexity and improve restoration.
With this solution you have fewer number of machine to manage, also server
including operating systems, applications, patches, are all encapsulated into a single virtual server; hardware is virtual and completely separated from the actual, physical hardware in the host server, this separation and encapsulation allow redundancy and restoration, as a virtual server can be restored on another host if necessary.
H. Security System
Physical and cyber security system should be established.
Refer to Directive on cyber security for network and Information
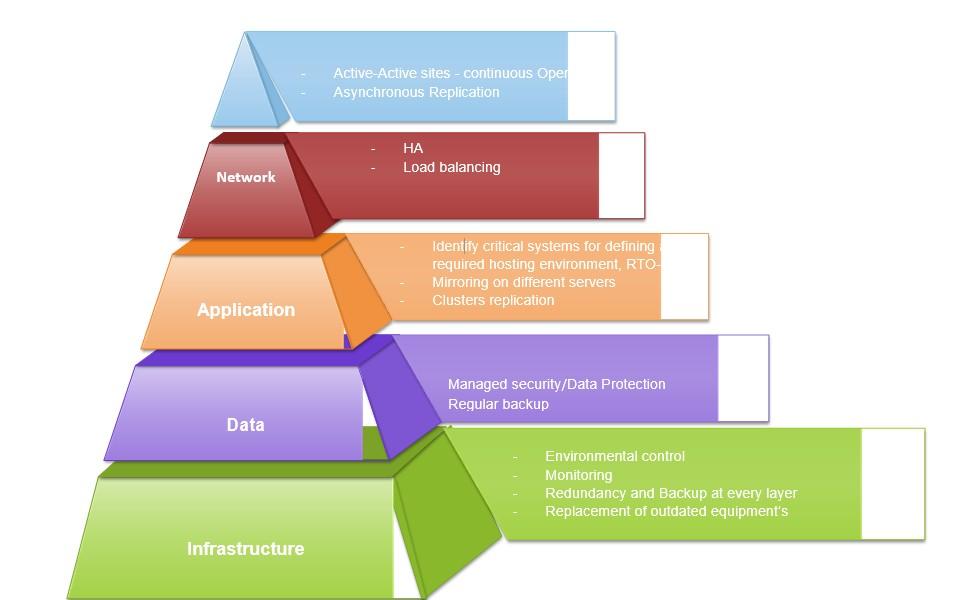
IT- Disaster Recovery Strategies
Figure 4: IT disaster recovery strategies
IT disaster recovery strategies encapsulate recovery solution at different layer
Disaster Recovery Phases
The main phases for responding to a disaster are:
- Deficiency/damage notification
- Analysis and evaluation
- Response and control of disaster (crisis management).
- Site rehabilitation and returning business to operating normal level.
- Documentation / Plan activation/update.
To ensure long-term viability and effectiveness of Business Continuity Plan, organization should maintain, conduct, and document a business continuity testing, training program regularly.
- Conducting a plan review at least quarterly
- Conduct continuity awareness briefings or orientations for entire workforce
- Train personnel on all reconstitution plans and procedures, recovery process.
- Test and validate equipment monthly to ensure internal and external interoperability, test viability of communications, alerts, notifications systems
- Test primary and backup infrastructure systems and services at primary and secondary recovery sites



No Comments