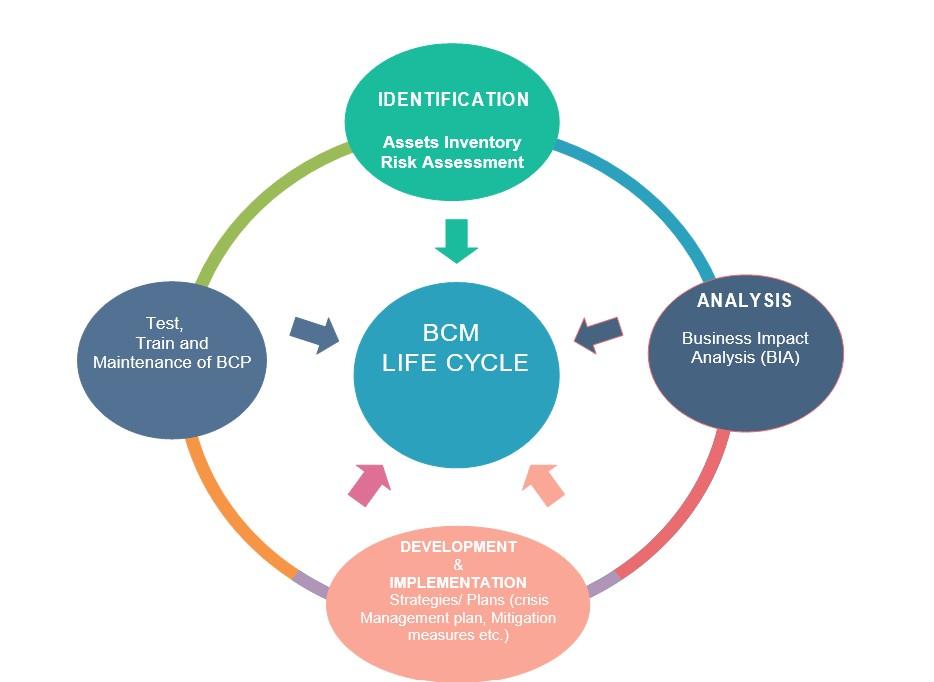
Business Continuity Management (BCM) Lifecycle
Business continuity management (BCM) is centred around a BCM lifecycle that consists of following phases:
Figure 2: Business Continuity Management Lifecycle
Identification: Assets Inventory And Risk Assessment
This phase is a starting point of BCM which allows an easy recognition of critical assets, categorization and prioritization based on criticality level.
- Assets inventory: consists of tracking, recording and managing all assets such as: (Infrastructure, systems, In-house software, Data, licenses, Company- owned equipment etc.).
- Risk Assessment: Consists of identifying and evaluating internal and external threats and vulnerabilities (risks), the likelihood, a control methods in place or required as well as the cost for such control.
Analysis: Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
BIA: is a fundamental phase from which a whole BCM process is built on; its central mission is to figure out which functions, systems and processes that are critical to an organization’s ongoing success, for a special management and protection.
BIA should be done as follows:
- Analyzing damage or outage impact: We do not only analyze a damage or outage impact and severity, but also a chronological sequence, looking at operational level, service level and financial level etc.
- Prioritizing: classification of functions/systems based on criticality level.
- Recovery parameters measurement: based on system criticality and chronological sequence of damaging events, a maximum tolerable period (MTP) of disruption, recovery time objective (RTO), and recovery point Objective (RPO) for each business function should be specified. For critical systems RTO and RPO should be minimized to zero.
- Determining required resources: Facilities, solutions and technologies that are needed for normal and emergency operation should be well defined.
Development and Implementation of Strategies - Plans
This phase consists of developing and implementing plans and strategies to follow in an immediate wake of an incident until damaged processes are fully restored.
Crisis Management Plan
Crisis management plan should contain:
- Crisis management structure (team with specific responsibilities): comprises of company’s President/CEO, heads of departments, technical team as well as vendors and external entities.
- A call tree to facilitate a quick and secure communication.
- HR and other facilities such as evacuation, alternative options. Etc.
Crisis Management Steps
Following crisis management steps are actions to be taken in the face of a major risks or crisis to allow a business to survive any crisis.
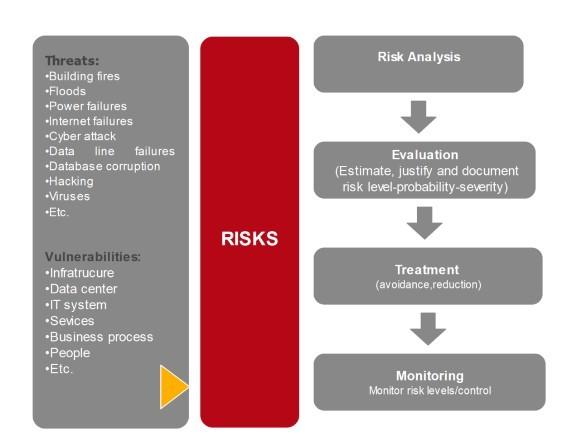
Figure 3: Crisis Management Steps
A. RISK ANALYSIS: consists of analyzing risk impact, likelihood and the effectiveness of countermeasures or control method in place.
B. RISK EVALUATION: This step consist of estimating, justifying, classifying and documenting risk severity level (Major, moderate or minor), risks that are internal - external, Risks with a direct - indirect effect.
C. RISK TREATMENT Following risk treatment options could be selected reliant on risk type:
- Assuming risk: This simply means that a risk is accepted; this option is selected when a probability of occurrence and potential damage is low or when a cost for an effective countermeasures is greater than a value of the assets to be protected.
- Risk transfer: this option consists of transferring risk management to another organization that has those capabilities. This can be done by signing an insurance policy or by outsourcing business process.
- Risk reduction: this option is selected for moderate risk, this is achieved by implementing measures, modifying and upgrading the process flow or system.
- Risk avoidance: this option is selected for critical functions of a business, where an organization examines well a probability of risk occurrence and reduce to zero a damage resulting from its occurrence.
D. RISK MONITORING: is an evaluation of effectiveness of risk management plan; and keep tracking new risks which ensures a control and an execution of a plan. Risk monitoring should be done regularly by performing a risk reassessment, risk registration updates, Technical performance or accomplishment measurement.

No Comments