Business Continuity Management (BCM) Lifecycle
Business continuity management (BCM) is centred around a BCM lifecycle that consists of following phases:
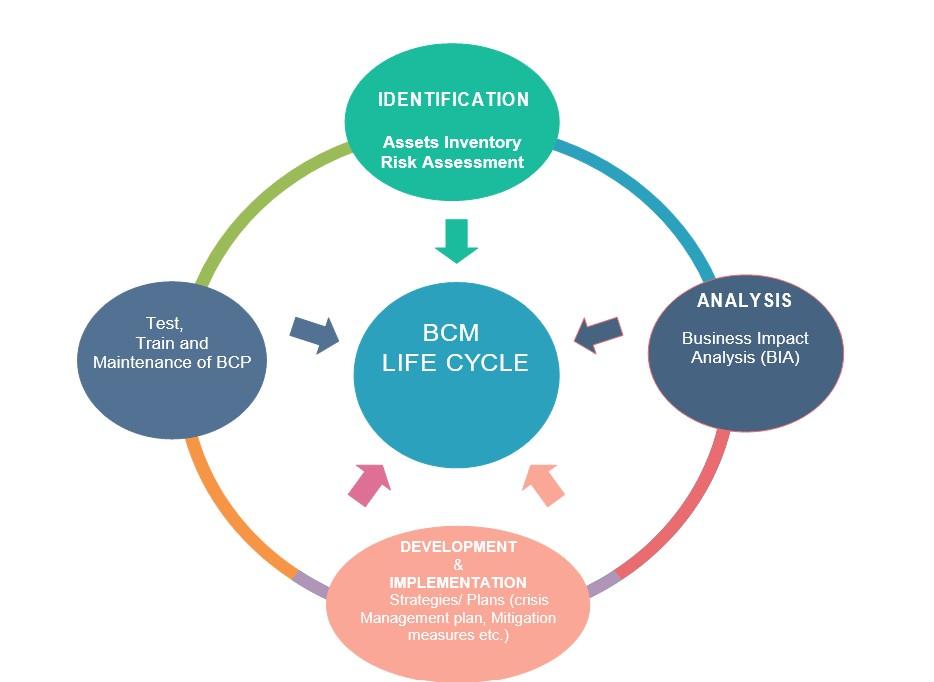
Figure 2: Business Continuity Management Lifecycle
Identification: Assets Inventory And Risk Assessment
This phase is a starting point of BCM which allows an easy recognition of critical assets, categorization and prioritization based on criticality level.
- Assets inventory: consists of tracking, recording and managing all assets such as: (Infrastructure, systems, In-house software, Data, licenses, Company- owned equipment etc.).
- Risk Assessment: Consists of identifying and evaluating internal and external threats and vulnerabilities (risks), the likelihood, a control methods in place or required as well as the cost for such control.
Analysis: Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
BIA: is a fundamental phase from which a whole BCM process is built on; its central mission is to figure out which functions, systems and processes that are critical to an organization’s ongoing success, for a special management and protection.
BIA should be done as follows:
- Analyzing damage or outage impact: We do not only analyze a damage or outage impact and severity, but also a chronological sequence, looking at operational level, service level and financial level etc.
- Prioritizing: classification of functions/systems based on criticality level.
- Recovery parameters measurement: based on system criticality and chronological sequence of damaging events, a maximum tolerable period (MTP) of disruption, recovery time objective (RTO), and recovery point Objective (RPO) for each business function should be specified. For critical systems RTO and RPO should be minimized to zero.
- Determining required resources: Facilities, solutions and technologies that are needed for normal and emergency operation should be well defined.
Development And Implementation Of Strategies - Plans